Spinal fractures are caused by trauma or conditions that weaken the bones.
Fractures can result from low or high energy trauma:
• A low energy fracture means it is the result of weakened bones, often due to osteoporosis, spine tumors or certain types of cancers. Low energy traumas usually result in stable fractures that can be treated using non-surgical methods.
• High energy fractures can be caused by a variety of traumas including car crashes, falls, sports accidents or acts of violence. A traumatic event can put too much pressure on the spine, and the vertebrae can break because they can’t withstand the force. They can result in both stable and non-stable fractures, depending on the type of damage caused to the vertebrae.
Symptoms of Spinal Fractures
Spinal fracture symptoms and the severity of those symptoms vary based on what type of spinal fracture you have and on whether the spinal fracture is causing nerve problems. A spinal fracture may cause sudden, severe pain and swelling around the area of injury. If the spinal fracture is pressing on a nerve or the spinal cord, you may have neurological symptoms such as:
• pain in back or neck that gets worse with motion, particularly when you are changing positions. It is often relieved by rest or lying down. Coughing and sneezing can also make the pain increase.
• pain that travels down your arms or legs (radiculopathy)
• weakness, numbness or tingling
• muscle spasm
• difficulty walking or moving
• bowel/bladder problems
• paralysis (in rare instances)
Note: Spinal fractures with neurological complications are especially serious, so if you have any of the above neurological symptoms—even if you don’t have pain—you should see a doctor as soon as possible. Always see a doctor after a traumatic event such as a car accident. Not all fractures cause spinal cord injury and rarely is the spinal cord completely severed.
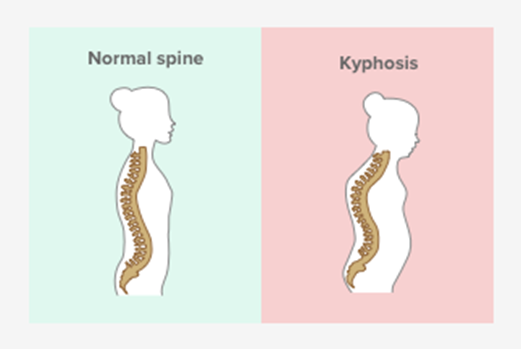
Compression fractures, a type of spinal fracture normally associated with osteoporosis or other conditions that weaken your bones, can involve additional symptoms. If, for example, you have multiple compression fractures, you can lose height or notice a hump in your spine (kyphosis).
Disclaimer – All information is for educational pursuit and information purposes only. It is not intended nor implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice. The viewer should always consult his or her healthcare provider to determine the appropriateness of the information for their own situation or if they have any questions regarding their medical condition, diagnosis, procedures, treatment plan, or other health related topic